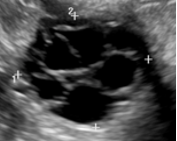
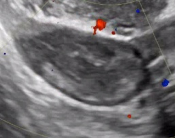
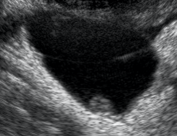
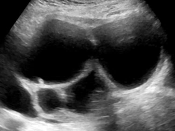
Adnexal Lesions: O-RADS US
Authors: Yang Guo, MD, Jessie Chai, MD, Carol Benson, MD, Atul Shinagare, MD
Date: January 11, 2021
| Category | Term | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
|
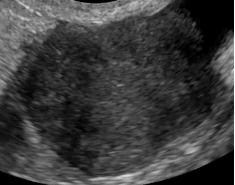
1. Major Categories A. Physiologic (consistent with normal ovarian physiology) |
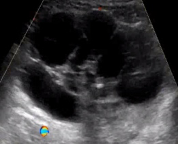
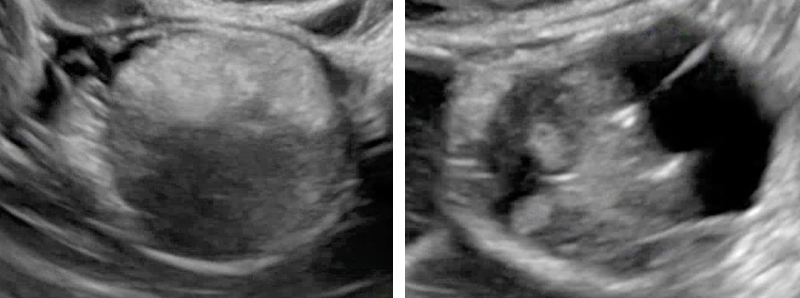
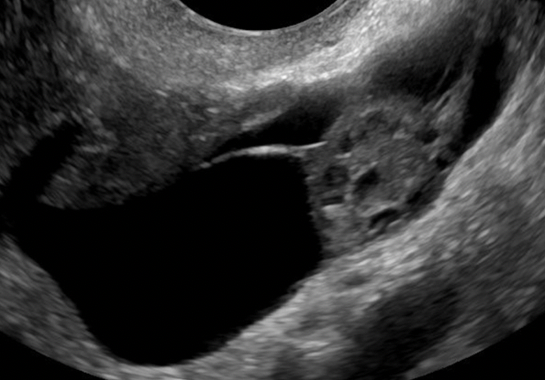
Follicle | Simple cyst ≤ 3 cm in premenopausal women | 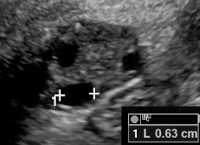 |
| Corpus luteum (CL) | *Thick walled cyst ≤3 cm that may have crenulated inner margins, internal echoes and intense peripheral flow *Sometimes may not have internal cystic space |  |
|
|
B. Lesion (Not consistent with normal ovarian physiology) |
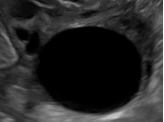
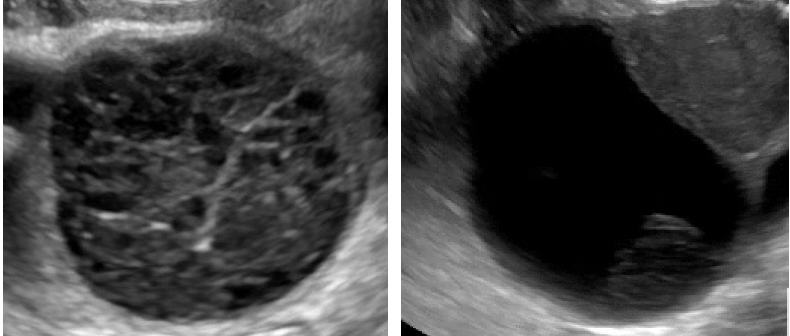
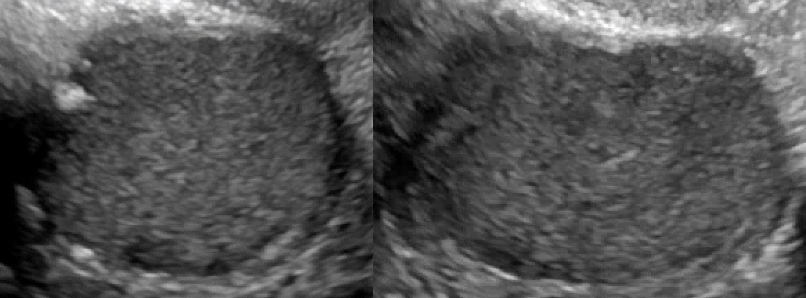
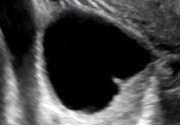
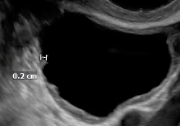
Unilocular, no solid component |
*Single compartment *May contain ≥ 1 incomplete septum *Wall irregularity < 3 mm height or internal echoes |
   |
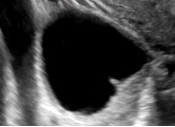
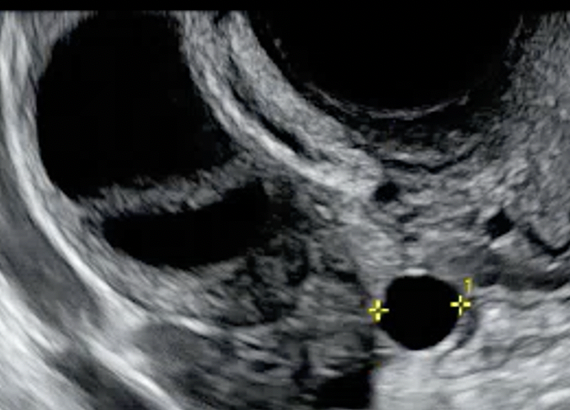
| Unilocular cyst with solid component(s) | As above, but includes solid component(s) ≥ 3 mm in height | 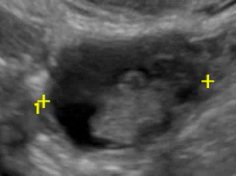 |
|
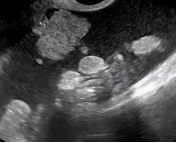
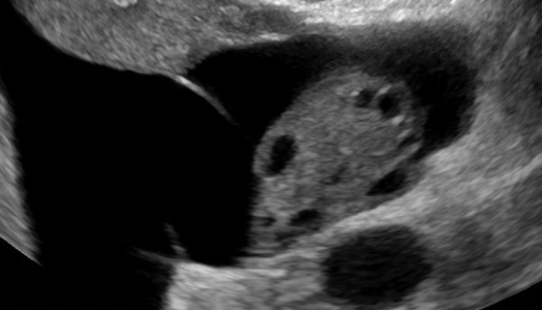
| Multilocular cyst, no solid elements | More than one compartment, but no solid component (s) |  |
|
| Multilocular cyst with solid component(s) | As above, but includes ≥ 1 solid component(s) ≥ 3 mm | 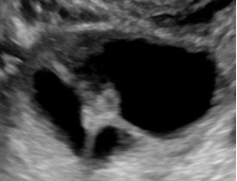 |
|
| Solid or solid appearing (≥80%) | At least 80% solid when assessed in orthogonal 2-dimensional plane | 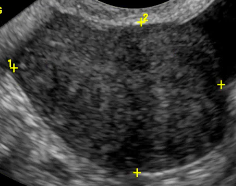 |
|
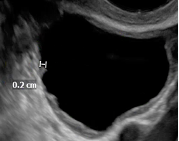
| 2. Size | Maximum diameter | Maximal diameter of the lesion in any plane | 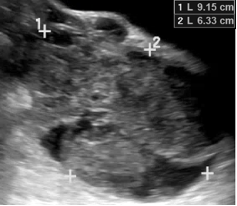 |
|
3. Solid or solid-appearing lesions A. External contour |
Smooth | Regular outer margin | 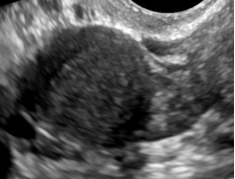 |
| Irregular (Not smooth) |
Non-uniform outer margin A lobulated outer margin is considered irregular |
|
|
|
B. Internal contents |
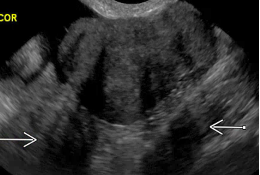
Acoustic shadowing |
Artifact produced by attenuated echoes behind a sound absorbing structure; commonly seen with calcification or fibromatous lesion |
 |
|
4. Cystic lesions: A. Internal margin or wall including solid component |
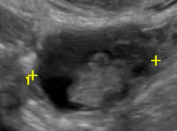
Papillary projection or nodule | Solid component whose height ≥ 3mm, arise from cyst wall or septation and protrudes into the cyst cavity | 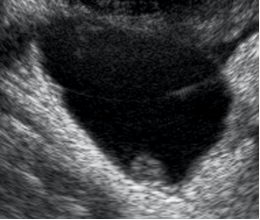 |
| Smooth |
Regular, uniform inner margin that may include inner margin of a solid component that is not a papillary projection |
|
|
| Irregular (Not smooth) |
*Irregular, non-uniform inner margin. May include wall irregularities due to incomplete septations, solid components < 3 mm height, papillary projections, the contour of the solid component or the margin of any internal cystic area within the solid component |
|
|
|
B. Internal content, cystic component |
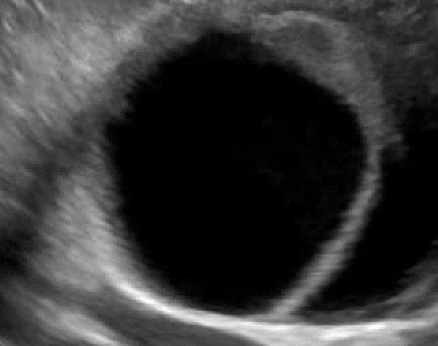
Anechoic fluid |
No internal echoes or internal structures of any kind |
 |
| Hyperechoic components |
Area of increased echogenicity relative to ovarian parenchyma without acoustic shadowing (seen with dermoid cysts or hemorrhagic lesions) |
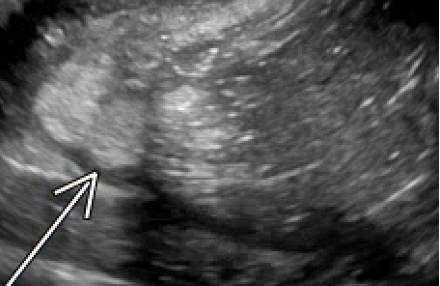 |
|
|
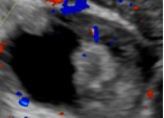
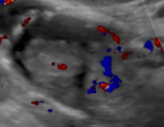
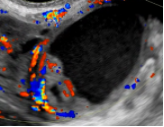
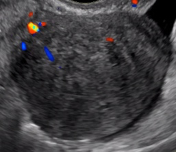
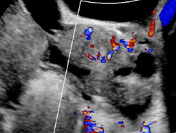
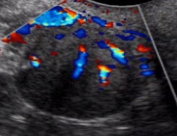
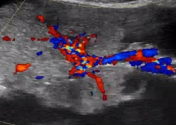
5. Vascularity Color score = Overall subjective assessment of color Doppler flow within entire lesion (wall and/or internal component) |
Color score = 1 |
No flow |
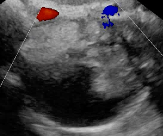 |
| Color score = 2 |
Minimal Flow |
|
|
| Color score = 3 |
Moderate Flow |
|
|
| Color score = 4 |
Very strong Flow |
|
|
|
6. General & Extra-Ovarian findings |
Fluid descriptors |
Cul-de-sac fluid |
 |
|
Ascites |
|
||
| Other |
Peritoneal thickening or nodules |
|
Utilizing US O-RADS Lexicon to Determine the Category of an Ovarian or Fallopian Tubal Lesion
- >Major categories: A. (Physiologic) or B. (Lesion)
- Size: Maximal diameter
- Solid or solid appearing lesions:
- A. External contour (smooth or irregular?)
- B. Internal contents (any acoustic shadowing present?)
- Cystic lesions:
- A. Inner margins or walls including solid component (any papillary projections or nodule? If so, how many? Is the inner wall smooth or irregular? Any solid components?)
- B. Internal content, cystic component (Any internal anechoic fluid or hyperechoic components present?)
- Vascularity: No flow, minimal flow, moderate flow or very strong flow (make sure scale for color is as low as possible while avoiding artifact)
- General and extra-ovarian findings: Free fluid (cul-de-sac fluid or ascites) and other (peritoneal thickening or nodule)
Risk Stratification and Follow Up Recommendatins
|
O-RADS Score and Risk Category |
Lesion Descriptors Examples |
Management | ||
|
Pre-menopausal |
Post-menopausal |
|||
| 0: Incomplete | N/A | Repeat or alternate study | ||
| 1: Normal | Follicle: simple cyst ≤ 3 cm | None | N/A | |
| Corpus luteum ≤3 cm | None | N/A | ||
|
2: Almost Certainly Benign [< 1%] |
Simple cyst |
≤3 cm | N/A | None |
| >3 cm to 5 cm | None | Follow up in 1 year | ||
| >5 cm but <10 cm | Follow up in 8-12 weeks | |||
| Classic Benign Lesions | See Section 3 | |||
|
Non-simple unilocular cyst, smooth inner margin |
≤3 cm | None |
Follow up in 1 year |
|
|
>3 cm but <10 cm |
Follow up in 8-12 weeks |
US specialist or MRI | ||
|
3. Low Risk Malignancy |
Unilocular cyst ≥ 10 cm (simple or non-simple) |
US specialist or MRI Gynecologist |
||
|
Unilocular cyst, any size with irregular inner wall < 3 mm height |
||||
|
Multilocular cyst < 10 cm, smooth inner wall, color score = 1-3 |
||||
|
Solid smooth, any size, color score = 1 |
||||
| Typical dermoid cysts, endometriomas, hemorrhagic cysts ≥ 10 cm (Section 3) | ||||
|
4: Intermediate risk [10 – <50%] |
Unilocular cyst with solid component: any size, 0-3 papillary projections, color score = any |
US specialist or MRI GYN-oncologist ± gynecologist |
||
|
Multilocular cyst, no solid component
|
||||
|
Multilocular cyst, with solid component: Any size, color score = 1-2 |
||||
|
Solid, smooth, any size, color score = 2-3 |
||||
|
5. High Risk [≥ 50%] |
Unilocular cyst: any size, ≥ 4 papillary projections, color score = any |
GYN oncologist |
||
|
Multilocular cyst with solid component: any size, color score = 3-4 |
||||
|
Solid smooth, any size, color score = 4 |
||||
|
Solid irregular, any size, color score = any |
||||
|
Ascites and/or peritoneal nodules |
||||
|
Classic Benign Ovarian Lesions |
|||
| Typical hemorrhagic cyst |
*Reticular pattern: Fine thin intersecting lines representing fibrin strands
|
Pre-menopausal |
Post-menopausal |
| ≤ 5 cm: none | US specialist, gynecologist or MRI | ||
| 5-10 cm: follow up in 8-12 weeks If persists or enlarges, referral to US specialist, gynecologist or MRI | |||
| Typical Dermoid cyst |
*Hyperechoic component with acoustic shadowing
|
* Optional initial follow up in 8-12 weeks based on certainty * If not removed, annual US follow up *US specialist or MRI if interval change |
*US specialist, gynecologist or MRI * If not removed, annual US follow up *MRI if interval change |
| Typical endometrioma |
*Ground glass or homogeneous low-level echoes
|
||
|
Classic Benign Extra-Ovarian Lesions |
|||
| Simple para-ovarian cyst |
Simple cyst separated from the ovary that typically moves independent of the ovary when pressure is applied by the transducer
|
Pre-menopausal | Post-menopausal |
|
*If simple, none *If not simple, manage per ovarian criteria |
*Optional single follow up ultrasound in 1 year | ||
| Typical Peritoneal Inclusion cyst |
Follows the contour of the adjacent pelvic organs or peritoneum, does not exert mass effect and typically contains septations. The ovary is either at the margin or suspended within the lesion
|
||
| Typical hydrosalpinx |
Incomplete septation, tubular
|
||
- Thomassin-Naggara I, Poncelet E, Jalaguier-Coudray A, et la. Ovarian-adnexal reporting data system magnetic resonance imaging (O-RADS MRI) score for risk stratification of sonographically indeterminate adnexal masses. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(1):e1919896.
- O-RADS MRI Lexicon Categories, Terms and Definitions. Release date: November 2002. https://www.acr.org/-/media/ACR/Files/RADS/O-RADS/O-RADS-MR-Lexicon-Terms-Table-November-2020.pdf
- O-RADS MRI Stratification System Table. Release date: September 2020. https://www.acr.org/-/media/ACR/Files/RADS/O-RADS/O-RADS-MR-Risk-Stratification-System-Table-September-2020.pdf